A velocity factor ( VF) is frequently quoted by vendors and used extensively in matching calculations. Here is the definition of the velocity factor for the uninitiated. The velocity factor is simply = 1/sqrt(relative permeability of the media X relative permittivity of the media). Generally the relative permeability is unity. So the velocity factor can said to be simply 1/sqrt( relative permittivity of the media). In other terms the VF of the media defines how a traveling wave is slowed down in the media compared to free space. More info please visit our website at www.signalpro.biz.
Category Archives: Uncategorized
RF Power amplifier: two tone testing
Two tone testing is used most often to test the linearity of a RF power amplifier ( or other amplifiers for that matter). The technique is fairly simple in principle but can have its little “gotchas”. First off, choice of frequencies. If you have 2.5 Ghz S band RFPA you are going to test, what frequencies do you use? Use frequencies close to 2.5 Ghz, say a few Mhz above and below or whatever provides the test results accurately ( simulations can be used to do this).Then the second issue is how do you generate the two tones to be input into the amplifier and not generate significant other IM products that will certainly destroy the test. ( A handy rule of thumb is to keep these input IMPs at least 6 dB below the test tones). Simple things like this can cause a real headache. My take is that if you are testing a 2.5 Ghz amplifier then you should place the two tones close to that frequency. Drive the amplifier so that the output at the tone will be close its rated output. Then measure using a good spectrum analyzer. ( Somewhat of a problem if you are a small company or hobbyist). Generally what will happen is that if the two tones are separated by f0 then the strongest two products will appear at f0 below the lower test tone and f0 above the higher test tone. Obviously there will be many more IM products that will be generated.
RF Power Amplifiers: Noise Power Ratio, NPR
Noise power ratio or NPR is a measure for a RF power amplifier ( among other analog circuits) that is usually used in the case of multicarrier power transmission using RFPAs. In order to understand NPR, it is instructive to basically describe how it is measured. First a white noise source is used and its output is passed through a band pass filter in the frequency band of interest. This represents multiple carriers with random amplitudes and phases. Then the resulting filtered signal is passed through a narrow, steep notch filter which is tuned to the frequencies of interest at the current measurement. First the output of this filter is passed through the DUT ( device under test) and the noise power is measured in the notch by using a narrow band receiver. Then the notch filter is bypassed and the noise power is again measured in the frequencies where the notch is using the narrow band receiver. The ratio of the two readings in dB is the NPR.
RF Power Amplifier Design: Conjugate matching and load line matching
A power amplifier device is characterized for a maximum operating current and a maximum operating voltage ( also see the safe operating areas of the device). A load line match is simply using the calculation: Vmax ( operating)/Imax(operating). This is the impedance that needs to be matched to if you want maximum performance out of the device. This is referred to in many books as the load line match. See also the paper in this blog on RF power amplifier design for a discussion of the load line. ( Go to www.signalpro.biz, go to complementary menu item, go to more reports, select RF Amp 1 paper), Conjugate match on the other hand refers to matching of the real parts of the generator and load with the reactance tuned out. See the book at :https://www.amazon.com/VSWR-Impedance-matching-techniques-electronic/dp/1490902813 for more details on this and other matching topics.
LC balun calculator
A LC balun balun calculator is now available for interested users on the Signal Processing Group Inc.’s website under the complementary menu item. Please scan through the items listed until you can select your choice. For background on LC baluns please read the post on LC baluns on the SPG blog. Use search to find it.
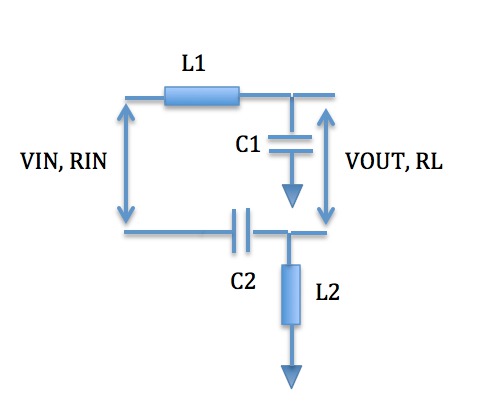
Balun design: A simple LC balun
One of the simplest baluns can be designed using L and C elements as shown below:
The design equations have been embodied in a Javascript calculator that will be provided in this blog for free download in the next post. Check back in a day or two to download the calculator. The input of this circuit is a balanced waveform and the impedance is set by the values of the L/C combinations. The output is another balanced signal with the required output impedance also calculated using the input and output impedances. This circuit may be implemented using discrete elements for use as a impedance transformer or a balun.
Please visit our website at www.signalpro.biz for more technical articles of interest and a description of our services.
Balun typical s parameters and their interpretation
The s parameters of a balun ( three port) are:
s12 = -s13 = s21 = -s31 and,
s11 = -infinity.
What does this mean in terms of conceptual understanding? The interpretation of these s parameter statements are:
- A balun is a three port device with a matched input and differential outputs.
- A balun is a three port power splitter
- The two outputs from a balun are equal in amplitude but opposite in phase.
- The voltage of one balanced output is the negative of the other balanced output.
- The input is matched to the input transmission line.
- The usual impedance is 50 Ohms. But it could be something else.
- A balun is a reciprocal device. Its output and inputs may be exchanged
For more technical articles and information please visit our website at: www.signalpro.biz.
Transmission line balun. What is it?
Simple baluns ( balanced-unbalanced) at lower frequencies use flux coupled transformers.They are generally limited to lower frequencies below 1 GHz. The reason is that at high frequencies the dipoles in the magnetic core cannot switch quickly enough, causing loss in the balun’s coupling between windings.
Parasitic capacitance between the windings leads to high frequency signals that pass directly to ground without coupling through the metallic core. Magnetic cores also have a large loss tangent. This causes high signal losses at microwave operation.
As a result of these effects, capacitance coupled transmission line baluns were invented. A transmission line balun is a set of coupled transmission lines with one end grounded. This type of coupling induces equal and opposite signals in both lines.
As a result of using a transmission line to connect to ground, the transmission line allows differential operation. Common forms of transmission line baluns include the 1:4 impedance ratio Ruthroff balun and 1:4 Guanella balun.
Please visit our website at www.signalpro.biz for more technical information and a description of our services..
RF power amplifiers: Class G and H basics
Class G and Class H are amplifiers with improved efficiency over the Class-AB amplifier. These amplifiers operate using tailored power supplies.. If high-output power is needed, a high-voltage power supply is supplied.. If the amplifier is low-power the supply voltage is reduced. These operations are automatically done.
An example program plan for ASIC/IC development
A good program plan can save a lot of time and expense in the development of ASICs/ICs as well as help towards a first pass success. We at Signal Processing Group Inc., have prepared an example of a plan based on an actual development, Please access this plan at www.signalpro.biz/progplan.pdf. Please note that contact points have changed. Please call 866-487-1119 for quick response to your requests or questions. Or contact us by email at spg@signalpro.biz.